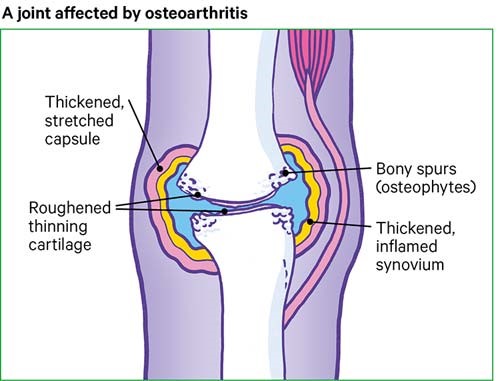
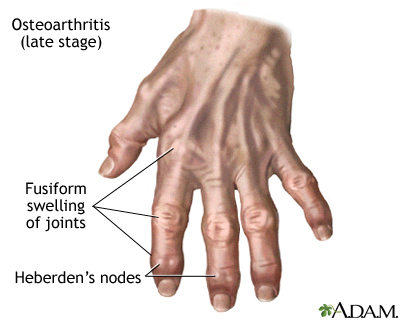
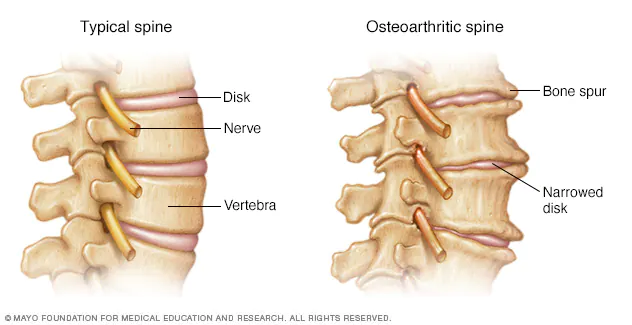
The main goal of osteoarthritis treatment is to improve the functionality of the patient by relieving the pain. Along with these physicians try to prevent the progression of osteoarthritis. Treatment plans often include a combination of drugs, rest, physical activity, joint protection, use of heat or cold to reduce pain, and physical or occupational therapy.
Weight loss: For every one pound of weight lost, there is a four pound reduction in the load exerted on the knee for each step taken during daily activities. It has also been shown that if a osteoarthritis patient loses 10% of weight the pain decreases by 50%.
Exercise: Exercise plays a very important role in the management of osteoarthritis. It has been shown consistently that quadriceps strengthening exercise is an integral step in the management of osteoarthritis .
Pain relievers: During acute exacerbation pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help reduce joint pain, stiffness and swelling. Drugs : Only supplement which has been proven to be effective in the management of osteoarthritis is Glucosamine. Most of other neutraceuticals have been disappointing in well conducted clinical trials, although manufactures claims are very high.
Surgery: Surgery in the form of joint replacement has seen major advances during last 2 decades. This is an important consideration in people with advanced Osteoarthritis associated with joint damage and/or marked limitations in joint function.